Types and Mechanism of Spot Grid
Spot grid mainly consists of arithmetic grid and geometric grid, which are suitable for narrow-range oscillations and wide-ranging trending markets, respectively. The bot operates in a four-stage cycle: initialization, arbitrage, dynamic adjustment, and termination. It is equipped with advanced features such as trailing grid, AI-powered parameter recommendations, HODL mode, and grid size progression mechanisms, all designed to enhance the bot's adaptability and profit potential.
1. Gate offers three methods to set up spot grid bot:
A. Ultra AI: Simply enter the investment amount to intelligently start executing the bot; suitable for beginners.
B. Recommended bots: Select a preferred active grid bot and directly copy it; ideal for beginners.
C. Manual configuration: Requires users to manually select trading pairs, price ranges, number of grids, investment amount, and other parameters. After confirming the settings, the bot starts running. It is suitable for experienced users.
2. Core categories of spot grid: arithmetic grid vs. geometric grid
Gate spot grid is divided into two types based on price interval calculation methods, tailored to different market volatility characteristics.
2.1 Arithmetic Grid
Mathematical principles: The price range is divided into equal parts by a fixed amount. The grid spacing is calculated as: Grid Spacing q = (Upper Limit Price a1 – Lower Limit Price a2) / (Number of Grids n−1)ROI Per Grid = q / Fill Price, and will change as the price moves.
Application scenario:
The price fluctuation is relatively stable (e.g., BTC/USDT fluctuates about $300 per hour).
- Low-volatility range market (Fluctuations < 30% of the coin price)
- Example: BTC range is $110,000–$120,000, with an arithmetic grid spacing of $1,000 and a fixed profit per grid.
2.2 Geometric Grid
- Mathematical principles: The price range is divided into equal ratios. The ratio coefficient is calculated as: Ratio Coefficient r = (Upper Limit Price a1 / Lower Limit Price a2) ^ ( 1 / (n-1))ROI Per Grid = r - 1, remains constant.
Application scenario:
Highly volatile coins (e.g., DOGE, SHIB, with daily fluctuations >10%)
- Wide-ranging sideways or trending markets (Fluctuations >50% of the coin price)
- Example: ETH price range is $2,000–$4,000, with a geometric grid spacing of 5%, placing large buy orders at lower prices to catch rebounds.
2.3 Comparison Table
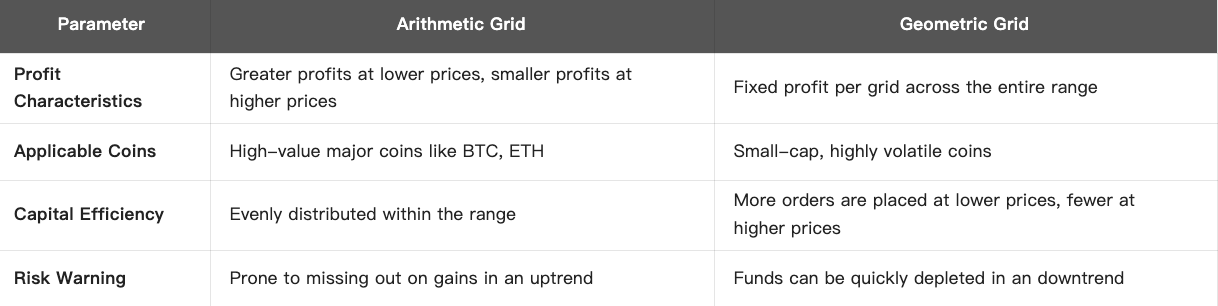
Conclusion: choose arithmetic grids for narrow-range oscillations and geometric grids for wide-range trends
3. Operating logic: four-stage automated cycle
The spot grid operates according to a closed-loop mechanism: initialization – volatility arbitrage – dynamic adjustment – termination
3.1. Bot Initialization
- Parameter settings: Users define the price range, number of grids, and investment amount; the system then automatically calculates grid lines and places limit orders.
- Order placement rules: Sell orders are placed above the current price, and buy orders below it; for example, if the BTC price is $100,000, sell and buy orders are placed at $101,000 and $99,000, respectively.
3.2. Volatility Arbitrage
- Trigger condition: Orders are automatically placed when the price reaches a grid line.
- Arbitrage cycle: Buy on the dip: when the price falls from $100,000 to $99,000, a buy order is executed and a sell order is placed at $100,000; sell on the rebound: when the price rises back to $100,000, the sell order is executed and a buy order is placed at $99,000.
- Profit formula: Grid Profit = Single-Grid Price Difference × Single-Grid Trading Volume × Number of Executions (Profit is constant for geometric grids, whereas it varies with price for arithmetic grids.
3.3. Dynamic Adjustment (Trailing Grid)
- Function logic: When the price breaks out of the original range, the grid automatically shifts to prevent bot failure: the entire range moves upward proportionally on an upward breakout and downward proportionally on a downward breakout.
3.4. Termination Conditions
- Normal termination: If the price remains outside the range and the trailing grid is not active, pending orders remain unfilled.
- Forced termination: TP Trigger: Price ≥ Upper Limit × 105% (e.g., $100,000 → $105,000); SL Trigger: Price ≤ Lower Limit × 95% (e.g., $50,000 → $47,500).
3.5. Gate Exclusive Features to Boost Bot Efficiency
AI-powered parameter recommendations:Based on 7-day historical data backtesting, the system automatically generates the optimal range and number of grids, enabling beginners to start with a single click.
HODL mode: Profits are automatically converted into the base currency (e.g., BTC), making it suitable for accumulating low-cost positions during the late stage of a bear market.
Grid size progression mechanism: Increase the trading volume of each grid proportionally (e.g., buy 1 BTC in the first grid, 1.2 BTC in the next) to reinforce positions in the direction of the trend.
