Gate Research: Prop AMM Revamp Solana liquidity
Summary
- Prop AMMs account for 20%-40% of Solana’s weekly volume, with over 80% in SOL-Stablecoin pairs.
- The proprietary fund model of Prop AMMs eliminates impermanent loss (IL), converting it into hedgeable inventory risk.
- Profitability does not rely on token incentives; Prop AMMs earn through spreads. Profit = total spread earned from market making - market value fluctuations of inventory assets - operating costs.
- As Solana evolves toward an on-chain CEX model, Prop AMMs will serve as core market makers.
I. The three iterations of AMMs
One of DeFi’s core innovations is the Automated Market Maker (AMM), which replaces the traditional order book model with mathematical formulas. However, the development of AMMs did not happen overnight—it has undergone three key iterations, each aimed at addressing the capital efficiency issues of the previous generation.
1.1 First Generation: Standard CPMM (Constant Product Market Maker)
The first generation of AMMs ushered in the DeFi era with their simplicity, but inherent design flaws limited their professionalism. Representative protocols include Uniswap V2 and Raydium (Legacy). At the core is the constant product formula x \ y = k, meaning the product of the two asset quantities x and y in the pool remains a constant k*.
A key feature of this type of AMM is passive market making. Liquidity is theoretically distributed evenly across the entire price range from 0 to ∞, ensuring that liquidity is available at any price point. The cost, however, is extremely thin depth distribution and very low capital efficiency—most of the capital is allocated to price ranges far from the current trading price, essentially in a “dormant” state and unable to be used effectively.
For example, in a SOL/USDC pool, even if the current price of SOL is 150 USDC, according to the formula, a large portion of the funds would still be allocated to price points like 1 USDC or 1,000 USDC for SOL, which are highly unlikely to be traded. This is akin to a convenience store with shelves full of drinks priced from 1 to 1,000 yuan, but customers only ever buy one or two of them—most of the inventory will never be sold.
At the same time, liquidity providers (LPs) must bear the risk of high impermanent loss (IL). Trading fees often cannot cover the IL, so LPs mainly rely on token rewards to offset losses caused by asset price fluctuations.
1.2 Second Generation: Concentrated Liquidity (CLMM)
To improve capital efficiency, the second generation of AMMs introduced the concept of concentrated liquidity, represented by Uniswap V3. It allows LPs to actively allocate capital within specific custom price ranges (e.g., only providing liquidity when ETH is priced between 2,900 and 3,000 USDC), thereby offering much higher liquidity depth than CPMMs within the target range. This innovation marked a major breakthrough—Uniswap V3’s launch was comparable to the iPhone moment in the DeFi space, becoming the dominant paradigm for DeFi liquidity.
However, CLMM shifts the responsibility and complexity of management entirely to the LPs. LPs need to behave like professional market makers, continuously forecasting price movements and manually adjusting their ranges. Once the price moves outside the specified range, the LP’s position is converted 100% into a single asset, effectively exiting market-making mode until the price returns or the range is manually reset.
This results in a fragmented user experience: the high returns are enjoyed by active managers with professional skills, while ordinary retail users either face a heavy management burden or suffer higher risks and lower returns due to poor range settings. While CLMM improves capital efficiency, it also deepens the gap between professional and amateur participants.
1.3 Third Generation: Active Management and Discrete Liquidity (Represented by Solana)
In the first two generations of AMM innovation, Ethereum and its leading DEX Uniswap were the primary drivers. However, in the current third-generation AMM revolution, Solana—with its high TPS, low transaction costs, and active on-chain activity—has become a more ideal testing ground. This generation pushes liquidity management to the extreme, enabling high-frequency, millisecond-level price adjustments that rival the efficiency of CEXs.
Thanks to Solana’s unique characteristics—high TPS, low gas fees, and a high-volume trading environment—its AMM development has split into two branches:
(1) Branch A: Public Active (Public DLMM), represented by Meteora Liquidity is discretized into a series of closely connected “price bins” (bin-based). It is transparent, permissionless, and still open to retail participants, who can manage positions through protocol-integrated algorithmic strategies. From a technical evolution standpoint, DLMM is a more elegant, user-friendly engineering implementation and productized extension of the CLMM concept, optimized for high-performance blockchains.
(2) Branch B: Private Institutional (Prop AMM / Dark Pools), represented by Humidifi and Tessera V In Prop AMMs, the “LPs” are no longer retail users, but professional market makers with large holdings. These systems are completely black-boxed, not relying on the on-chain constant product formula x \ y = k* for pricing. Instead, they use external oracles and internal algorithms, directly mapping CEX-style matching engines and inventory management logic onto the blockchain to pursue the highest possible trade execution quality.
Overall, the evolution of AMMs has moved from offering thin liquidity everywhere to providing deep liquidity exactly where it’s most needed. Prop AMMs represent another milestone in this efficiency race—delivering professional, on-chain market-making services powered by institutional capital.
II. Definition and Mechanism of Prop AMMs (Dark Pools)
The emergence of Prop AMMs marks a key shift in on-chain market-making strategies—from being driven by mathematical models to being driven by professional trading logic. Essentially, it brings high-performance market makers’ (MMs) trading desks directly on-chain, leveraging Solana’s low-latency environment to enable high-frequency, low-slippage trade execution.
2.1 Definition and Boundaries
Prop AMMs refer to on-chain trading venues where liquidity is fully controlled by professional market makers, pricing algorithms are not publicly disclosed (or partially computed off-chain), and there is typically no frontend interface. Due to their internal operations being opaque to the public, they are often referred to as Dark AMMs or Private Market Makers. Major Prop AMMs on Solana include HumidiFi, Tessera V, GoonFi, ZeroFi, and SolFi.
I. Solana Prop AMMs Volume
2.2 Why Is It Called “Prop” (Proprietary)?
“Proprietary” is key to understanding how this type of AMM operates:
(1) Proprietary Funds: The liquidity in these AMMs is 100% provided by the project team or the professional market makers behind them (in some cases, the project team itself comes from a market-making background). They do not accept public deposits, completely overturning the traditional DeFi model where liquidity is supplied by retail users.
(2) Proprietary Strategies: The trading strategies—how to quote, when to cancel orders, how to hedge—are core trade secrets of the market makers. These strategies are not written into smart contracts for public review. Instead, calculations are done off-chain, and only the final trading instructions are submitted on-chain for settlement, similar to proprietary trading desks in traditional finance.
2.3 Technology and Operating Mechanism
Prop AMMs are able to deliver market-making performance on-chain that rivals CEXs by relying on a carefully integrated tech stack that combines high-performance off-chain computation with on-chain priority execution.
2.3.1 “Oracle + Solver” Hybrid Pricing Model: Off-Chain Computation, On-Chain Execution
Prop AMMs do not rely on the on-chain ratio of assets in a pool to determine pricing. Instead, they use a hybrid pricing model that separates price computation and trade execution:
(1) Off-chain computation — the private Solver as a decision-making black box
When a quote request is initiated by the Jupiter aggregator, the market maker’s backend Solver is triggered and performs the following off-chain computations within milliseconds: first, it retrieves a reference price by subscribing to and monitoring data streams from oracles such as Pyth, acquiring real-time fair market values directly provided by first-party institutions like exchanges and market makers and aggregated off-chain; using the oracle price as input, the Solver runs its proprietary algorithmic model to compute the final quote, which incorporates factors such as inventory risk, volatility and market sentiment, order flow toxicity prediction, and real-time costs; the algorithm then outputs a deterministic quote that includes at least the price, token amount, and a validity timestamp. This entire process is executed on off-chain servers, with the strategies, parameters, and calculations kept private.
(2) On-chain execution — atomic and protected settlement
Once the off-chain computation is complete, the system seamlessly transitions to the on-chain execution phase: the Solver submits the computed quote to the Solana network via a signed transaction, the core of which calls the Prop AMM’s on-chain smart contract to update the current valid quote in its state; to ensure this new quote is prioritized, the protocol may pay higher priority fees to Jito validators—effectively bidding for top-of-block execution on optimized networks like Jito—ensuring the quote is confirmed before regular user transactions and protected from arbitrage during propagation; after aggregators compare quotes across the network, if a Prop AMM offers the best one, the user’s trade is routed to its contract, which atomically verifies two key conditions: whether the current market price (typically still checked via oracle) remains within the quote’s promised valid range, and whether the user’s trade size does not exceed the quoted amount; if both checks pass, the user’s asset and the market maker’s quoted asset are exchanged in the same transaction and block, with the market maker earning the spread and the user receiving the asset—this entire process is either fully successful or fully reverted, with no partial state.
2.3.2 Traffic Entry: Parasitic on Aggregators (Jupiter)
Prop AMMs operate in a “headless mode,” with their sole user entry point being top aggregators like Jupiter. This forms a parasitic relationship—Jupiter must search for the best price for each user trade request, querying all available liquidity sources across the network, including Raydium, Orca, Meteora, and various Prop AMMs.
All the competition happens within Jupiter’s routing algorithm, essentially a millisecond-level price war. For every quote request, the “brain” of a Prop AMM must respond within milliseconds. Only if its quote is at least equal to or consistently better than that of public pools like Raydium, Orca, or Meteora will the trade be routed to it. This design forces Prop AMMs to engage in highly efficient market making—any strategic misstep or technical delay can result in lost traffic.
As a result, Prop AMMs and aggregators form a deeply symbiotic relationship: the former rely on the latter to access users, while the latter rely on the former to deliver best-in-class pricing to stay competitive.
2.3.3 MEV Resistance and IL Elimination
Prop AMM’s risk management operates on two fronts: externally, it has active defenses against harmful order flow and MEV; internally, its proprietary capital model fundamentally transforms market-making risk by converting uncontrollable IL into manageable inventory risk.
In public AMMs, liquidity acts as a passive public utility and is vulnerable to being exploited by MEV bots. In contrast, Prop AMMs turn liquidity into an active “predator,” flipping from defense to offense. First, by paying higher priority fees, Prop AMMs ensure their quote updates and transactions are always included first, ahead of attacking bots, making front-running technically infeasible. Second, the off-chain Solver can analyze trade characteristics in real time; for orders from known arbitrage addresses or those exhibiting typical arbitrage patterns (e.g. trailing large trades, precise sizing), the Solver can choose to either not respond or offer a wide, unprofitable quote—effectively denying service.
Finally, Prop AMMs typically adopt a Just-In-Time (JIT) liquidity strategy. After winning a trade via an aggregator, they instantly allocate the necessary assets from their own vaults within the same atomic transaction or a tightly sequenced set of instructions, then immediately withdraw. This minimizes capital exposure time, drastically shrinking the attack window for MEV bots attempting sandwich attacks.
II. HumidiFi Asset Composition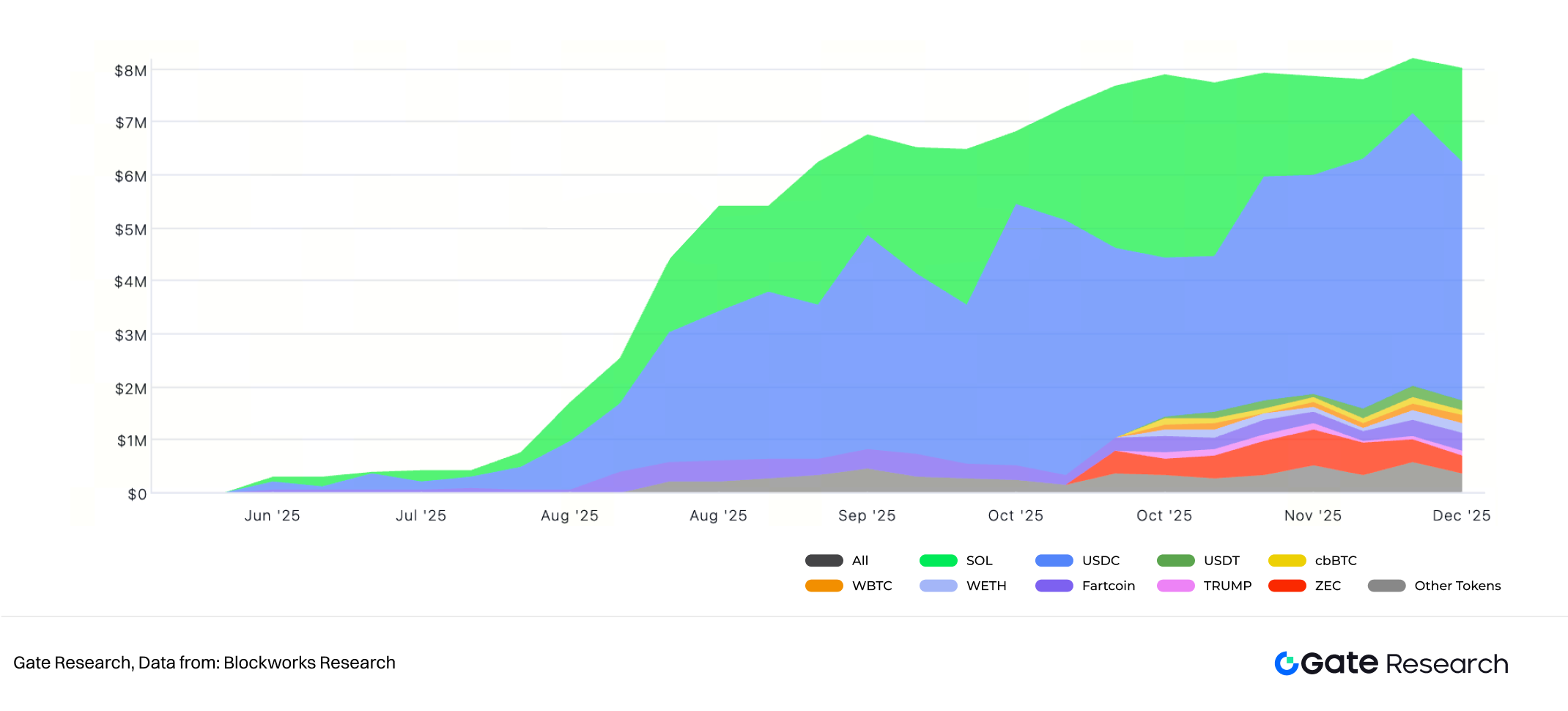
Moreover, Prop AMMs hold a major advantage over traditional LPs by transforming the risk of IL. In a Prop AMM, the protocol uses proprietary capital, and its goal is not to maintain a constant asset ratio, but to continuously generate spread income through active quoting. Inventory fluctuations—for example, holding more USDC and less SOL during a bull market—are a natural outcome of market-making activities, not a “loss.” Therefore, the traditional concept of impermanent loss becomes irrelevant here, replaced by inventory risk.
The protocol manages inventory dynamically through its Solver algorithm to keep it within a target range. This may involve active hedging or external balancing—for instance, if inventory becomes heavily skewed, the protocol team can hedge on a CEX to quickly rebalance overall risk exposure.
The protocol’s final PnL = total spread earned from market-making – market value fluctuations of inventory assets – operating costs.
This is an active, professionally managed profit-and-loss model, rather than the passive, decision-independent IL borne by traditional LPs.
III. Market Landscape and Leading Players
The rise of Prop AMMs is not an isolated event, but a reflection of the profound structural transformation taking place in the Solana DEX market. Since the beginning of this year, Solana DEX trading activity has shifted from meme-driven speculation to a focus on SOL-Stablecoin pairs. Currently, SOL-Stablecoins consistently contribute 60%-70% of Solana DEX volume, creating a vast opportunity for active market-making strategies to thrive.
III. Solana DEX Volume
3.1 The Ecological Role of Prop AMMs in Solana
Prop AMMs have grown at a remarkable pace this year, with several major Prop AMMs reaching a cumulative volume of over $270 billion. Currently, Prop AMMs account for 20% to 40% of Solana DEX weekly volume.
IV. Solana DEX: Prop AMM vs Traditional DEX (SOL-Stablecoins Pairs (right))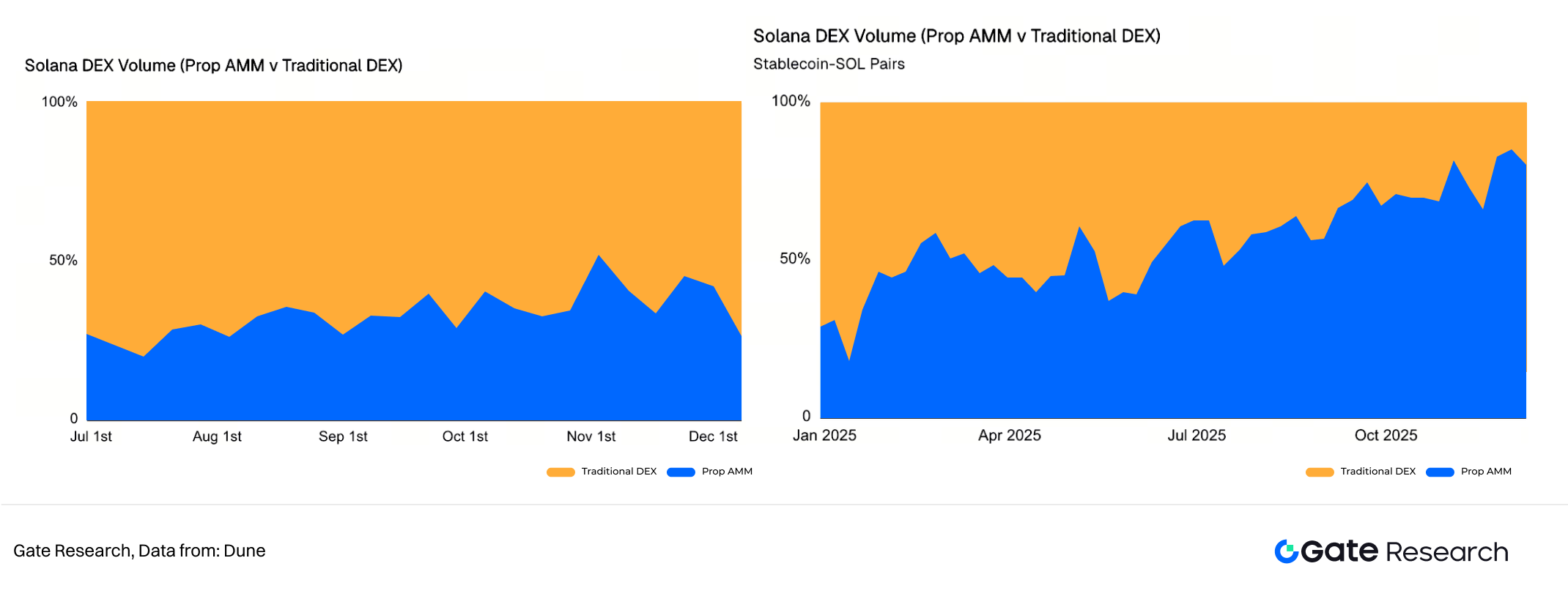
Especially in SOL-Stablecoin pairs, Prop AMMs have clearly secured a strategic position as Solana’s top execution layer, capturing over 80% of the market share. In large trades (over $100k) involving SOL-Stablecoins, Prop AMMs overwhelmingly outperform traditional AMMs in terms of slippage. This is because their liquidity depth is modeled after CEX infrastructure, rather than relying solely on on-chain TVL.
3.2 Major Players and Competition in Prop AMMs
Within the Prop AMM sector, significant performance gaps exist due to differences in strategies and risk management models.
V. Solana Prop AMM Volume Market Share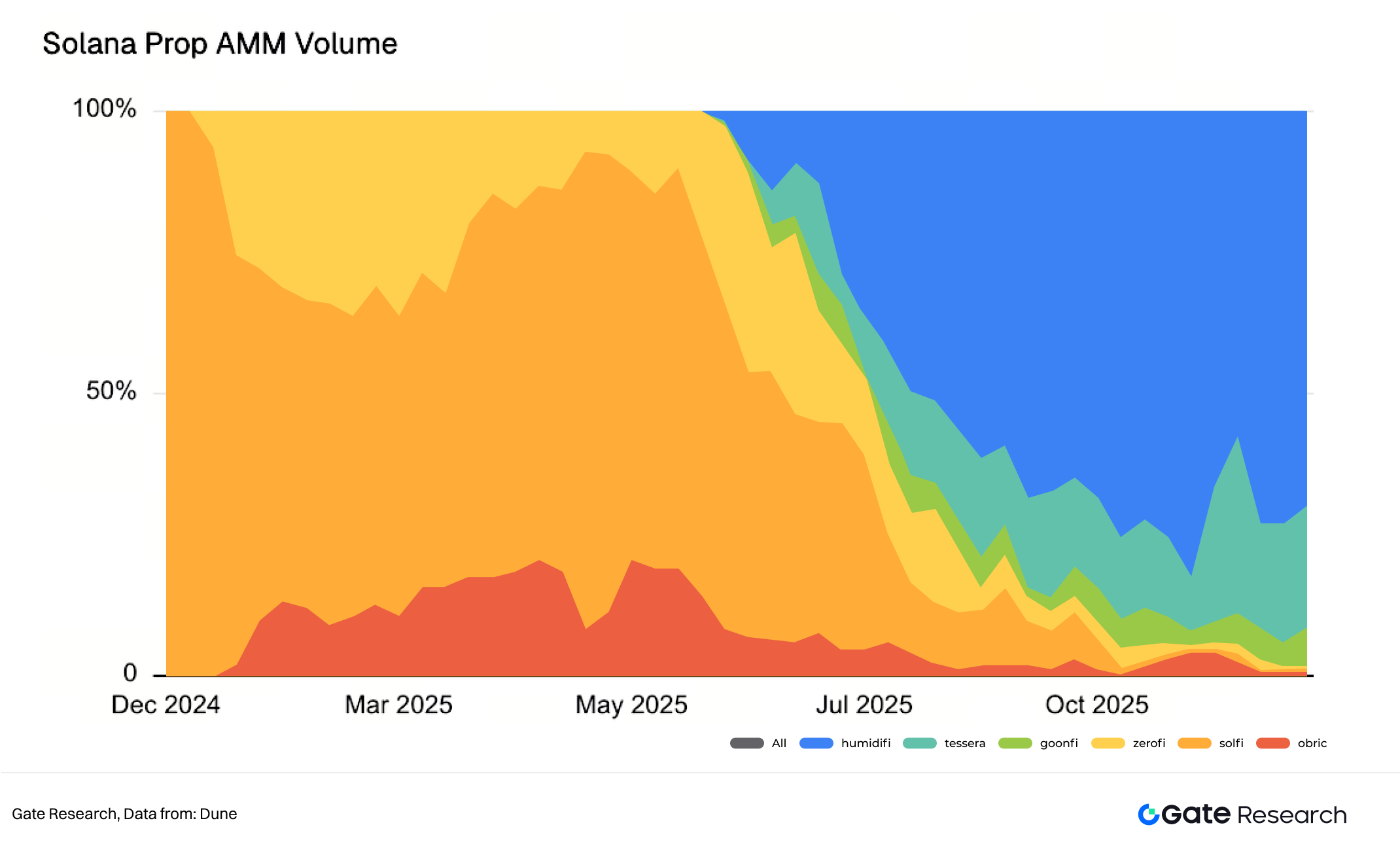
Since its launch in late June, HumidiFi has rapidly become the largest Prop AMM—and even the largest DEX—on Solana, also becoming the first Prop AMM to surpass $100 billion in cumulative trading volume. Currently, HumidiFi maintains a daily trading volume of over $1 billion, holding more than 60% market share among Prop AMMs.
The key reason lies in the core competitiveness of Prop AMMs: the number of trading pairs they support, the proprietary strategies of the team behind them, and the effectiveness of their black-box pricing curves. The ability to minimize spread is crucial.
VI. Active Token Pairs across Prop AMMs
Although Prop AMM trading volume is primarily concentrated in core pairs like SOL-Stablecoins, new protocols are beginning to expand their quoting capabilities to include more long-tail assets in order to compete for aggregator routing priority and attract a broader flow of orders. For example, Aquifer, launched in September, offers quotes for as many as 190 trading pairs—more than the combined total supported by other Prop AMMs. Similarly, ZeroFi, HumidiFi, and AlphaQ are actively expanding their service boundaries to include top memecoins (such as Fartcoin and USELESS) and cross-chain assets from third-party networks (such as MON and ZEC).
That said, the core value of a Prop AMM still lies in the minimal size of its spreads and the stability with which they are maintained.
VII. Solana DEX Execution Spread (USDC-WSOL)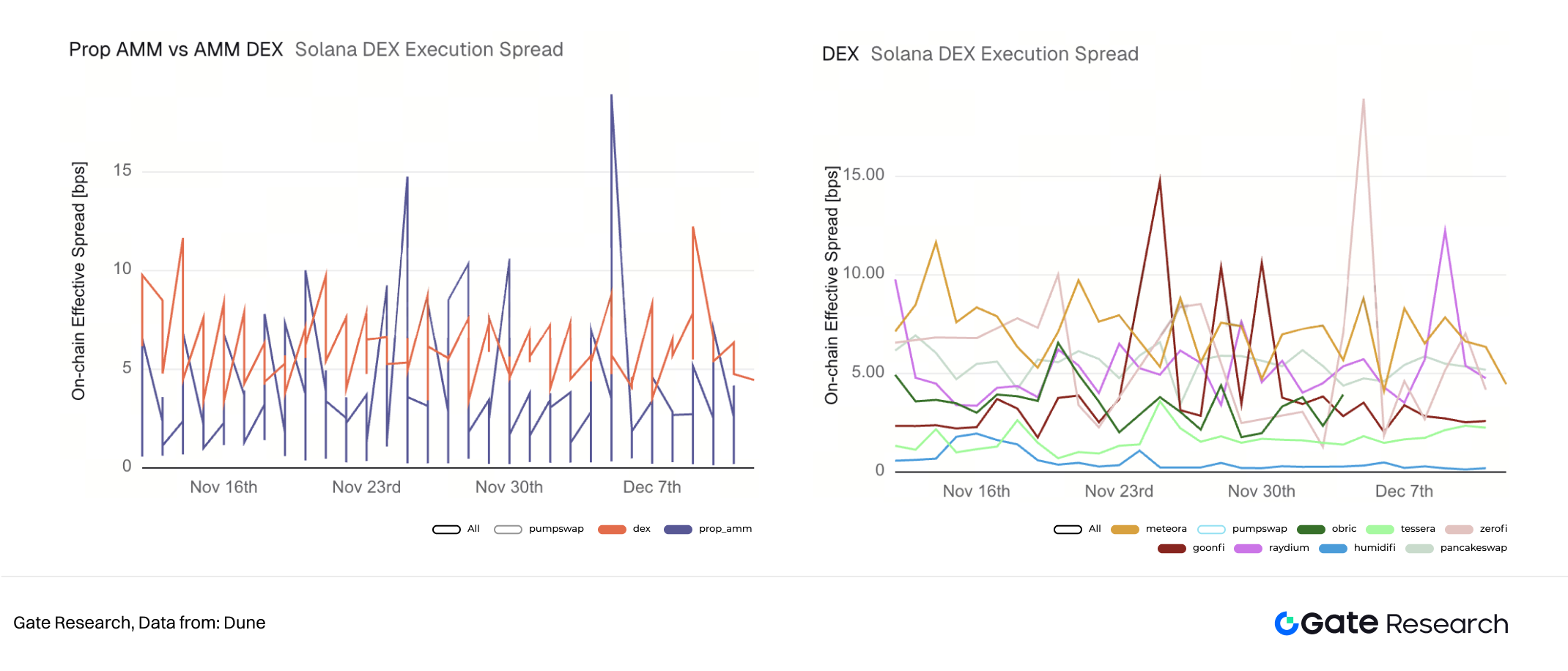
A review of the past month’s SOL/USDC trading data shows that while Prop AMMs offer lower average spreads overall, they carry higher tail risk—primarily due to significant internal variance among different Prop AMMs. In contrast, mainstream DEXs like Meteora and PancakeSwap tend to have higher average spreads but offer much greater stability, reflecting their stronger technical infrastructure and operational capabilities.
Within the Prop AMM space, Tessera V and HumidiFi stand out for their spread stability. Tessera V maintains spreads around ~2bps, while HumidiFi pushes the limit even further, keeping spreads under 1bps—this is a key factor behind its leading position. In contrast, GoonFi and ZeroFi show much greater volatility, with spread fluctuations spiking above 15bps.
It’s also worth noting that competition in the Prop AMM sector is intensifying. There are now at least eight players operating dark pool-style businesses, compared to just two at the beginning of the year. The token launch strategy of Prop AMMs has also become a focal point for valuation discussions. HumidiFi, the largest Prop AMM dark pool, was the first to issue a token. Launching at the peak of its business may secure a higher market valuation and premium. From a competitive standpoint, if new entrants were to launch tokens earlier, it could negatively impact HumidiFi’s perceived value—so the leader moving first can be seen as a preemptive strategy in response to rising competition.
However, the design of HumidiFi’s tokenomics—such as its utility, value accrual mechanisms, and overall role within the ecosystem—remains unclear. This lack of clarity is a central topic of concern and discussion among the community and investors.
IV. Economic Model and Ecosystem Impact
Prop AMMs have fully departed from the early DeFi model of token incentives and liquidity mining, instead adopting the profit logic of traditional finance—namely high-frequency trading (HFT) and professional market making. Their impact on the Solana ecosystem is a double-edged sword.
4.1 Profit Model
The sustainability of Prop AMMs does not rely on external incentives but is instead built directly on their superior execution efficiency and risk management capabilities.
The primary revenue source for Prop AMMs comes from spreads—the small difference between bid and ask prices—essentially the same profit mechanism used by market makers on centralized exchanges (CEXs). With extreme execution efficiency and active hedging, in theory, even narrow spreads can generate solid profits when combined with high daily trading volumes and ultra-low operational costs. However, due to the opaque nature of Prop AMMs and the lack of publicly available data, some community members remain skeptical about whether HumidiFi, which operates with spreads compressed below 1bps, can actually produce meaningful profits.
In addition, to maintain top pricing positions within aggregators, protocols may consider offering rebate incentives—via tokens or fee-sharing structures—to aggregators or specific order flow providers. This could become one of the main motivations behind token issuance for Prop AMMs.
Fundamentally, a protocol’s final PnL still boils down to: Total spread revenue from market making – market value fluctuations of inventory assets – operating costs, which forms a proactive, professionally-driven profit-and-loss model.
4.2 A Double-Edged Sword for the Solana Ecosystem
The impact of Prop AMMs is complex—representing yet another classic trade-off in DeFi history between efficiency and fairness, openness and opacity.
For users, Prop AMMs offer a near CEX-like experience: virtually zero slippage and deep liquidity, especially benefiting large traders. By shifting market making from the hands of countless retail LPs to a small number of highly efficient professional players, the overall capital efficiency and pricing accuracy of the market are, in theory, significantly improved.
However, behind this revolution in efficiency and user experience lies a more disruptive, systemic challenge. Prop AMMs are capturing the largest volumes and the most profitable spreads in major trading pairs. As their coverage of trading pairs continues to expand—as expected—this will directly reduce the earnings of traditional LPs in public pools like Raydium and Orca. The longer-term risk is that if traffic and revenue continue to be siphoned away, public liquidity pools will gradually shrink, relegated to serving only long-tail assets or extreme market conditions. This could erode DeFi’s foundational principles of openness and permissionlessness.
The opacity of Prop AMMs lies not only in the lack of a frontend but also in the anonymity of the teams behind them. If liquidity and pricing power increasingly concentrate in anonymous or institutional hands, new centralized points of control could emerge. Strategy failures, technical bugs, or malicious behavior could trigger severe on-chain market disruptions. Additionally, DeFi thrives on composability. The closed interfaces and dynamic logic of Prop AMMs may make them difficult to safely and reliably integrate into other DeFi protocols—such as lending, derivatives, or automated vault strategies.
V. Conclusion and Outlook
The rise of Prop AMMs is not merely a technical optimization—it marks the institutionalization and professionalization of on-chain trading on Solana, representing liquidity providers’ ultimate pursuit of capital efficiency.
In the future, the final form of Prop AMMs may be to serve as the professional market makers of Solana as a “on-chain CEX”. Their emergence is steering Solana’s DEX market structure toward the traditional financial exchange model—where order flow heavily depends on a few specialized market makers. Solana is gradually evolving into a transparent settlement layer CEX, and Prop AMMs function as its trading desks, delivering the lowest latency and best execution quality.
While users enjoy the efficiency gains brought by Prop AMMs, this also forces traditional public AMMs to pursue design innovation—enabling regular LPs to access more professional, automated market-making strategies. This could allow public and institutional liquidity to coexist, rather than seeing retail LPs fully marginalized. For traders, this shift means trading behavior may gradually move away from interacting with individual DEXs toward relying more on aggregators, in order to fully benefit from the minimal slippage and optimal execution that Prop AMMs provide.
VI. Reference
- Dune, https://dune.com/the_defi_report/prop-amms
- Blockworks, https://blockworks.com/analytics/humidifi/humidifi-tvl
- Dune, https://dune.com/sliceanalytics/solana-dex-activity
- Dune, https://dune.com/queries/6266421/9988032
- The Block, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LPQGl6Ju16U
Gate Research is a comprehensive blockchain and crypto research platform that provides readers with in-depth content, including technical analysis, hot insights, market reviews, industry research, trend forecasts, and macroeconomic policy analysis.
Disclaimer
Investing in the cryptocurrency market involves high risk. Users are advised to conduct independent research and fully understand the nature of the assets and products before making any investment decisions. Gate is not responsible for any losses or damages arising from such investment decisions.
Related Articles

Gate Research: 2024 Cryptocurrency Market Review and 2025 Trend Forecast

How To Claim The Jupiter Airdrop: A Step-By-Step Guide
Solana Staking Simplified: A Complete Guide to SOL Staking

Gate Research: BTC Breaks $100K Milestone, November Crypto Trading Volume Exceeds $10 Trillion For First Time

Introduction to Raydium


