Trade
Basic
Futures
Futures
Hundreds of contracts settled in USDT or BTC
TradFi
Gold
Trade global traditional assets with USDT in one place
Options
Hot
Trade European-style vanilla options
Unified Account
Maximize your capital efficiency
Demo Trading
Futures Kickoff
Get prepared for your futures trading
Futures Events
Participate in events to win generous rewards
Demo Trading
Use virtual funds to experience risk-free trading
Earn
Launch
CandyDrop
Collect candies to earn airdrops
Launchpool
Quick staking, earn potential new tokens
HODLer Airdrop
Hold GT and get massive airdrops for free
Launchpad
Be early to the next big token project
Alpha Points
Trade on-chain assets and enjoy airdrop rewards!
Futures Points
Earn futures points and claim airdrop rewards
Investment
Simple Earn
Earn interests with idle tokens
Auto-Invest
Auto-invest on a regular basis
Dual Investment
Buy low and sell high to take profits from price fluctuations
Soft Staking
Earn rewards with flexible staking
Crypto Loan
0 Fees
Pledge one crypto to borrow another
Lending Center
One-stop lending hub
VIP Wealth Hub
Customized wealth management empowers your assets growth
Private Wealth Management
Customized asset management to grow your digital assets
Quant Fund
Top asset management team helps you profit without hassle
Staking
Stake cryptos to earn in PoS products
Smart Leverage
New
No forced liquidation before maturity, worry-free leveraged gains
GUSD Minting
Use USDT/USDC to mint GUSD for treasury-level yields
More
Promotions
Activity Center
Join activities and win big cash prizes and exclusive merch
Referral
20 USDT
Earn 40% commission or up to 500 USDT rewards
Affiliate
Enjoy exclusive commissions and earn high returns
Announcements
Announcements of new listings, activities, upgrades, etc
Gate Blog
Crypto industry articles
VIP Services
Huge fee discounts
Proof of Reserves
Gate promises 100% proof of reserves
TradFi
Connect stocks, metals, commodities, forex, and indices
Asset Management
New
One‑stop asset management solution
Institutional
New
Professional digital asset solutions for institutions
OTC Bank Transfer
Deposit and withdraw fiat
Broker Program
Generous API rebate mechanisms
Gate Vault
Keep your assets secure
TRON Industry Weekly Report: BTC Rebounds to $70,000 After Major Drop, Detailed Explanation of AI-Guarded Full-Chain Interoperability L1 Zenchain
I. Outlook
Last week, after several weeks of high-level trading, the US stock market began to focus on digesting the reality of still-strong employment and the repeated postponement of rate cut expectations. High valuations and high positions quickly turned into pressure sources in the absence of new positive catalysts. Market sentiment shifted directly from “hesitation” to “defensive,” with technology and high-growth sectors leading the sell-off. The index experienced a sharp decline with increased volume, indicating that this was not a normal correction but a emotional stampede triggered by collapsing expectations and loosening positions.
Looking ahead, this decline seems more like a forced correction of overly optimistic expectations. In a macro environment where there is no obvious deterioration but policy easing remains delayed, the US stock market will find it difficult to quickly return to the previous unilateral upward trend. High volatility may become the norm.
Last week, the cryptocurrency market entered a phase of high volatility and extremely fragile sentiment. Bitcoin experienced a technical rebound at $60,000, but overall remained in a clearly weak zone. Trading volume stayed high, indicating ongoing deleveraging and ongoing battles between bulls and bears, with incomplete clearing.
From a risk perspective, the current market resembles a consolidation phase after a crash rather than a trend stabilization. As long as Bitcoin cannot quickly return and stabilize above key resistance zones, any rebound could be seen as a window for reducing positions. Altcoins and high-volatility sectors still face ongoing selling pressure. Meanwhile, macro-level adjustments to interest rate expectations may continue to impact the crypto market through sentiment and liquidity channels. Overall, in the short term, caution is needed for potential secondary declines or prolonged low-level consumption, and true stability signals are still to be observed.
Total funding of $2 million led by CMS and Stonewood Capital—River, a bridge-free cross-chain stablecoin liquidity layer that enhances multi-chain capital efficiency, is building a chain-abstracted stablecoin system to connect different ecosystems; total funding of $5 million, with Mint leading and 90S participating, DeepNode is a decentralized intelligent infrastructure platform supporting AI models to be deployed, executed, and verified in permissionless, low-trust, modular environments with incentive mechanisms.
II. Market Hot Sectors and Weekly Potential Projects
1.1. Brief Analysis of $2 million Total Funding Led by CMS and Stonewood Capital—River, a Bridge-Free Cross-Chain Stablecoin Liquidity Layer
Introduction
River is building a chain-abstracted stablecoin system to connect liquidity across different ecosystems. Its core product is satUSD based on omni-CDP: users can deposit collateral assets on one chain and mint satUSD on another—without cross-chain bridges or asset wrapping.
This design achieves true cross-chain capital efficiency, allowing liquidity to flow seamlessly across multi-chain ecosystems.
Core Mechanism Summary
1. Omni-CDP
River integrates LayerZero’s cross-chain communication technology to create the first Omni-CDP (full-chain collateralized debt position) protocol. Users can deposit BTC on one chain and directly mint satUSD on another, enabling seamless liquidity across multiple blockchains without traditional cross-chain bridges or asset wrapping.
2. satUSD+
satUSD+ is the core yield token in River’s yield layer. After staking satUSD, users automatically convert to satUSD+, maintaining liquidity and composability while continuously earning a share of the protocol’s real income.
satUSD staking mechanism:
Users stake stablecoins supported by excess collateral such as BTC, ETH, BNB, and LST, participate in River’s yield layer, and earn a proportional share of protocol fees.
The essence of satUSD+:
ERC-20 form of liquidity income token
Automatically accumulates protocol income without manual claiming or re-investment
Can be redeemed for satUSD at any time
Can be used in other DeFi protocols (lending, LP, etc.)
Income sources (non-inflationary):
Omni-CDP: minting, redemption, liquidation fees
System-wide usage: satUSD in multiple chains and applications
Future modules: lending markets, partnership incentives, on-chain revenue sharing
3. River4FUN
River4FUN is River’s contribution incentive layer, designed to reward influence and participation, not just capital.
Core concept:
Most protocols only reward capital, but River4FUN incorporates attention, content, and dissemination into the incentive system, transforming them into real protocol ownership.
Operation:
Connect wallet and X (Twitter) account
Post content related to River or partner projects (tweets, replies, quotes)
Earn River Points based on exposure, interaction quality, and consistency
Periodic points update
All River Points are exchanged for $RIVER at TGE
System significance:
River4FUN completes the full flywheel of River:
Mint → Stake → Post
4. Smart Vault
Smart Vault is River’s one-click yield module, emphasizing zero liquidation risk and sustainable income. Users only need to deposit assets to continuously earn yield without managing positions or worrying about market fluctuations triggering liquidations.
Problems solved:
In traditional DeFi, users often face a trade-off between earning yield and maintaining safety, with frequent management of collateral ratios and liquidation monitoring. Smart Vault automates these strategies, eliminating these complexities.
Core advantages:
Zero liquidation risk: assets are not forcibly liquidated
No position management: no need to monitor collateral ratios or health
Sustainable income: derived from real strategy yields, not inflation
Asset security: 1:1 deposit and withdrawal, assets can be retrieved at any time
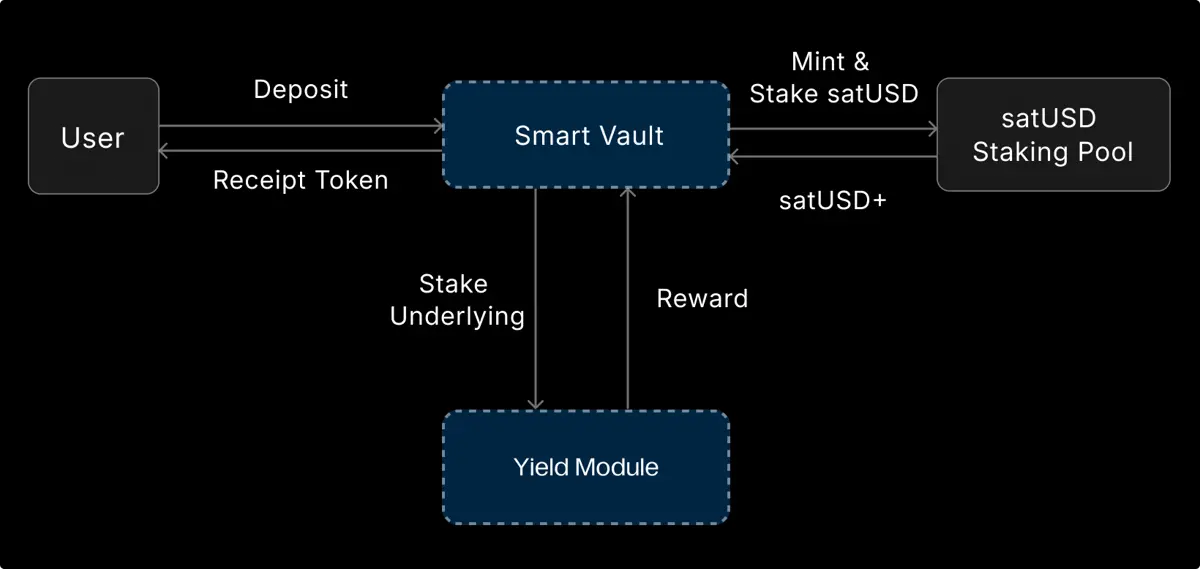
Operation mechanism:
Users deposit BTC, ETH, USDT/USDC → protocol automatically mints satUSD based on value → satUSD directly enters the staking pool → underlying assets are deployed to DeFi / CeDeFi / RWA yield scenarios via strategy modules → users continuously earn yields.
Throughout the process, satUSD circulates within the protocol and does not enter user wallets, avoiding liquidation risks.
5. Prime Vault
Prime Vault is River’s institutional-grade yield treasury designed for institutional users, ensuring the highest level of asset security and compliant custody, providing predictable and sustainable stable returns while minimizing operational complexity and risk exposure.
Problems addressed:
Eliminates forced liquidation risks caused by market volatility
Meets high standards of compliance and asset security for institutions
Reduces technical and operational burdens for institutional DeFi participation
Core advantages:
Institutional-grade security: partnered with top custody institutions and listed companies, assets are always in regulated custody wallets
Zero liquidation risk: automated internal position management to avoid any form of liquidation
No smart contract risk: underlying assets are not exposed to complex DeFi contracts, avoiding code and hacking risks
Predictable returns: continuous income based on River stablecoin yield system
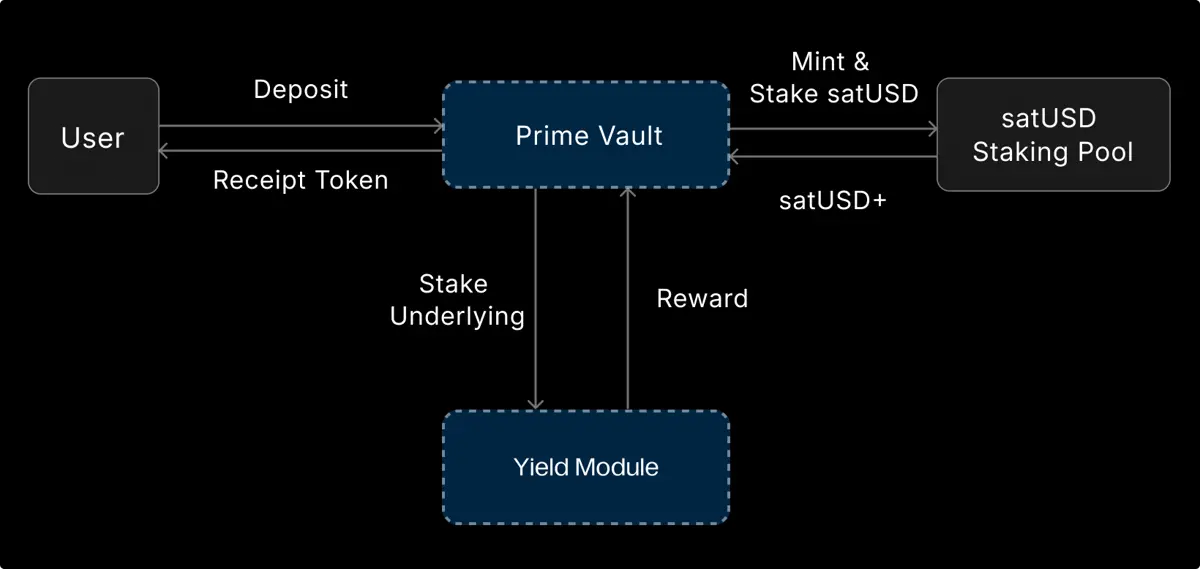
Operation mechanism:
Institutions deposit assets like BTC → assets are locked in secure custody wallets → protocol internally mints satUSD based on asset value → satUSD enters the staking pool for yield → upon maturity, principal and accumulated yield are withdrawn.
Throughout the process, users do not incur liabilities, and satUSD does not enter user wallets.
Architecture and risk control parameters:
Custody integration: assets are always held by regulated custodians
Internal satUSD system: only used for staking and yield distribution
Smart position management: automatically adapts to deposits, withdrawals, and market fluctuations
Governance parameters: set by $RIVER holders for asset-level staking ratios (0–100%)
Periodic rebalancing: adjusted based on oracle data to ensure yield operation without compromising principal safety
Tron Review
River’s core advantage lies in its highly differentiated chain-abstracted stablecoin system: through Omni-CDP and LayerZero, it achieves “bridge-free, wrapping-free” cross-chain minting of satUSD, significantly improving multi-chain capital efficiency; satUSD+, Smart Vault, and Prime Vault form a comprehensive yield product matrix from retail to institutional, balancing zero liquidation risk, real protocol income, liquidity, and compliant custody; River4FUN incorporates influence and content contribution into the incentive loop, creating a complete flywheel of Mint → Stake → Yield → Contribute.
Potential disadvantages include system complexity, high reliance on cross-chain communication and custody partners, and the fact that yield scale and long-term stability depend heavily on satUSD’s cross-chain adoption and protocol real usage. There are certain execution and expansion risks before the ecosystem matures.
1.2. Interpretation of $5 million Total Funding Led by Mint and 90S—DeepNode, a Decentralized Global AI and Computing Power Market
Introduction
DeepNode is a decentralized AI network where intelligence no longer belongs to a few giants but to all contributors. It is an open AI marketplace: developers worldwide can contribute AI models, computing power, and data, and receive fair rewards based on the real value they create.
DeepNode aims to transform AI from a monopolized resource into a democratized public infrastructure—owned and operated collectively by those truly advancing AI development.
Architecture Overview
DeepNode is a decentralized intelligent infrastructure platform supporting AI models to be deployed, executed, and verified in permissionless, low-trust, modular environments with incentive mechanisms. The platform connects model developers, compute providers, verifiers, and users via the $DN token, forming a unified AI value network, replacing centralized intermediaries with on-chain coordination.
Open participation: anyone can be a model creator, executor, verifier, staker, or user
On-chain transparency: model registration, task execution, reputation scoring, and reward distribution are all on-chain
Modular roles: participants can choose or combine different roles based on ability
Built-in redundancy: multiple nodes execute the same AI tasks in parallel, ensuring verifiability and fault tolerance
Performance-based incentives: rewards based on accuracy, efficiency, online rate, and other quantifiable metrics
Gradual decentralization: starting from a whitelist, gradually transitioning to DAO governance for a fully open network
Model Marketplace
Decentralized model registration and monetization layer, ensuring model ownership transparency and fair income distribution
Execution Layer
Distributed compute network, nodes run AI models and earn $DN rewards based on verification tasks
Validation Layer
Validates and scores model outputs, maintaining network trustworthiness
Reputation Layer
Records participant performance on-chain, influencing task assignment, weights, and rewards
Governance Layer
Community-driven protocol upgrades and key decision mechanisms
Domain Layer
Supports specialized sub-networks (sub-domains) operating independently while anchored to the DeepNode main network
Incentive Mechanism
DeepNode’s incentive system revolves around the $DN token, covering staking, bonding, access rights, payments, governance, and reward distribution. This mechanism is tightly coupled with platform roles and value flows, forming the economic foundation for efficient network operation.
DeepNode adopts a domain (sub-network) level incentive model
Each domain has independent incentive configurations
Domain owners decide:
Revenue sharing
Token emission/distribution
2. Key Participant Incentives
Domain owners set incentive rules for core roles:
Miners: execute AI tasks, provide compute power
Validators: verify model outputs, maintain network trustworthiness
Creators & Backers: provide AI models, data, or early support
3. Summary of Mechanism Highlights
Highly modular and configurable incentives
Different domains can customize economic models based on application scenarios
Rewards and token emissions are directly linked to actual contributions and performance
Tron Review
DeepNode’s advantage is in its unification of AI models, compute power, and data into a decentralized marketplace. Through verifiable on-chain execution, multi-node redundancy, reputation systems, and domain-level configurable incentives, it enables fine-grained pricing and fair distribution of real AI contributions; the $DN token underpins execution, verification, governance, and payments, avoiding empty incentives, and its modular architecture facilitates rapid expansion in vertical AI scenarios.
Its disadvantages include high system complexity, higher demands on execution efficiency, verification costs, and network coordination. Early-stage reliance on domain owner parameter design and governance could impact compute quality and ecosystem launch speed if incentives are misconfigured.
2.1. Detailed Analysis of $8.5 million Total Funding Led by DWF and Genesis—Zenchain, a Fully Interoperable Layer 1 Connecting Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Future Multi-Chain Worlds with AI Guardians
Introduction
Zenchain is a Layer 1 blockchain designed to achieve trustless, low-trust-cost cross-chain interoperability with Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other ecosystems. Based on the BARK (Blockchain Architect Resource Kit) architecture, Zenchain employs a validator-protected Cross-Liquidity Consensus Mechanism (CLCM) to provide cryptoeconomic security for transactions.
On the execution layer, Zenchain natively supports EVM for smart contract deployment and integrates WebAssembly (Wasm) dApps via precompiles, bridging EVM and native Wasm runtimes. Its cross-chain interoperability module (CCIM) supports secure cross-chain asset transfers and interactions; the innovative ZIP-20 token standard offers a more flexible asset management framework.
Additionally, Zenchain integrates Niō (AI-driven on-chain guardian) for real-time threat detection and mitigation, enhancing network resilience and security; it also supports non-fork upgrades, promoting continuous stability and innovation in cross-chain communication and decentralized computing.
Architecture Summary
Zenchain aims to build a high-security, scalable, highly interoperable Layer 1 blockchain. Based on the BARK framework, it combines advanced consensus mechanisms, flexible runtime environments, and comprehensive client support to enable smooth cross-chain interactions and dApp development.
The core consensus design, the Cross-Liquidity Consensus Mechanism (CLCM), balances security, decentralization, and efficiency. CLCM involves validators and nominators working together to maintain network integrity, with staking and incentive mechanisms encouraging broad participation and enhancing overall security.
Validators: verify transactions, produce blocks, and finalize blocks, selected based on their or nominated ZTC stake. They earn rewards through staking; malicious behavior or poor performance results in slashing, making their stable performance critical for network security.
Nominators: support validators by staking tokens, sharing rewards, and bearing risks—if supported validators are penalized, nominators’ stakes are also reduced, incentivizing careful selection of reliable validators.
Overall, CLCM uses economic incentives and risk-sharing to strengthen Zenchain’s decentralization and security, providing a solid consensus foundation for cross-chain and application ecosystems.
Zenchain employs a hybrid consensus model combining RAGE for block production and GUARDIAN for finality confirmation, blending probabilistic finality with provable finality to ensure high performance and irreversible security.
Hybrid Consensus Design
Probabilistic finality (RAGE): ensures blocks can be produced continuously and rapidly without network stalls.
Provable finality (GUARDIAN): validators vote to confirm chain state; once finalized, blocks cannot be reverted.
This division balances high throughput with strong security.
Block Production: RAGE
Epochs and Slots: the network operates in epochs, each containing multiple slots (~6 seconds each).
Random block production: each slot uses a probabilistic lottery to select validators eligible to produce a block.
Multiple validators can produce blocks in the same slot; the fastest propagated block is accepted.
No validator fallback: if no one is selected in a slot, a polling mechanism ensures continuous block production.
Finality Component: GUARDIAN
Voting finality: validators vote over multiple rounds; when over 2/3 confirm a chain, it and its previous blocks are finalized at once.
Chain-level finality: unlike block-by-block confirmation, GUARDIAN reaches consensus on the entire chain, allowing quick recovery after network fluctuations.
Security: in partially synchronous networks, as long as 2/3 of validators are honest, finality is achievable, tolerating some Byzantine nodes.
Fork Choice and Collaboration
RAGE always produces blocks on top of the chain head finalized by GUARDIAN, forming a clear fork choice rule to avoid following incorrect forks and overcoming potential stagnation in pure finality systems.
2. Staking Mechanism
Positioning: Staking is core to Zenchain’s Cross-Liquidity Consensus Mechanism (CLCM), securing the network and incentivizing participation.
Cycle Structure:
Era: about 6 hours, settling rewards and penalties for validators and nominators.
Session: sub-cycle within an era (~1 hour), rotating validators and evaluating performance.
Participation:
Bonding: locking ZTC tokens for consensus participation.
Staking: acting as validator or nominator.
Unbonding: withdrawing stake, with a lock-up period.
Fast-Unstaking: quick exit under certain conditions, with a deposit.
Role division:
Validators: produce blocks, verify transactions, participate in finality votes, rewarded based on performance, penalized for misconduct (Slashing).
Nominators: delegate stake to support validators, share rewards, and bear joint risks.
Auxiliary mechanisms:
Chilling: temporarily pause staking without unlocking assets.
Rewards: distributed based on actual performance during an era, independent of stake size.
Claiming: rewards must be actively claimed.
Slashing: penalizes malicious or low-performance behavior.
Election mechanism:
Uses Phragmen algorithm to select and balance validator set at each era start.
3. Runtime Mechanism
Overall positioning: Zenchain’s runtime supports both Ethereum ecosystem and native BARK modules, enabling diverse dApp development.
EVM Compatibility:
Integrates SputnikVM for Ethereum-compatible smart contracts
Supports Ethereum JSON-RPC
Existing Ethereum dApps can deploy without modification
BARK Native Modules (Wasm Modules):
Based on Wasm, native to the chain
High performance, flexible
Supports integrating complex functions directly into the runtime
Precompiles:
Connect EVM and BARK native modules
Provide native access to functions for EVM
Enable efficient cross-VM interactions
JSON-RPC Interface:
Unified client interaction entry point
Supports both Ethereum and BARK-specific methods
Covers contract deployment, queries, transactions, and state management
Overall Design
Core Module: Cross-Chain Interoperability Module (CCIM)
Features: Chain-agnostic, unified management of inbound and outbound cross-chain transactions
Goal: Achieve secure, efficient interoperability between Zenchain and chains like Ethereum and Bitcoin
Advantages:
Abstracts the complexity of different chains
Provides standardized interfaces
Highly scalable and adaptable
Inbound Cross-Chain Transactions
Process Overview:
Outbound Cross-Chain Transactions
Process Overview:
Overall Positioning
Niō is Zenchain’s built-in AI-driven security guardian system
Uses decentralized AI + real-time monitoring to identify and defend against threats before escalation
Aims to provide continuous, adaptive on-chain security protection
Core Capabilities
Real-time security monitoring: continuously scans on-chain activity and ecosystem behavior
Decentralized security intelligence: avoids single points of failure
Machine learning + heuristic analysis: counter evolving attack methods
Proactive defense: intervenes before or early in attacks
Niō Guardians (Modular Security Protectors)
Niō adopts a modular design, allowing flexible expansion of new Guardians based on attack types.
Deployed core Guardians include:
Scam Guardian: detects and warns of new scam behaviors
Attack Guardian: real-time detection and mitigation of protocol-layer attacks
Spam Guardian: filters spam tokens and NFTs, maintaining ecosystem quality
Rug Pull Guardian: identifies malicious code patterns to prevent Rug Pulls
Sybil Guardian: defends against Sybil attacks, ensuring identity system integrity
Tron Review
Zenchain’s advantage lies in its integrated Layer 1 design centered on cross-chain interoperability: through CLCM consensus and the RAGE + GUARDIAN hybrid mechanism, it achieves fast block production with provable finality; native EVM compatibility combined with Wasm/BARK runtime enables efficient coexistence of Ethereum applications and native modules; CCIM provides standardized, bidirectional cross-chain capabilities covering Bitcoin, Ethereum, and more ecosystems; Niō AI adds real-time security, giving the network a differentiated edge in security and maintainability.
Potential disadvantages include high architectural complexity (multiple consensus components, runtimes, cross-chain modules), higher demands on validators, developers, and early governance, and the fact that cross-chain and AI security capabilities need time to verify long-term stability and cost efficiency under large-scale real loads.
III. Industry Data Analysis
1. Overall Market Performance
1.1. Spot BTC vs ETH Price Trends
BTC
ETH
2. Hot Sector Summary
IV. Macro Data Review and Key Data Release Schedule for Next Week
Important macro data releases this week:
February 10: US December Retail Sales Monthly Rate
February 11: US January Unemployment Rate; US January Non-Farm Payrolls (Seasonally Adjusted)
February 13: US January Unadjusted CPI Yearly Rate
V. Regulatory Policies
China: Issuance of Comprehensive Risk Prevention Notice
On February 5, 2026, China’s eight ministries jointly issued the “Notice on Further Preventing and Disposing of Risks Related to Virtual Currencies and Other Assets,” significantly upgrading regulatory measures.
Policy core: The notice explicitly bans all virtual currency and real-world asset tokenization activities, classifying them as illegal financial activities, and requires financial institutions, payment agencies, and internet companies not to provide related services.
New regulatory scope: In addition to virtual currencies, it explicitly includes real-world asset tokenization activities, with strict supervision of domestic entities engaging in related overseas activities.
Law enforcement coordination: Emphasizes establishing a central-local joint working mechanism to crack down on illegal financial and criminal activities.
US: Progress in Legislation and Regulatory Coordination
This week, the US made clear progress in crypto legislation and regulatory coordination.
Legislation process: On January 29, the Senate Agriculture Committee passed its version of the “Digital Asset Market Structure Act” by a vote of 12-11. The bill aims to expand the Commodity Futures Trading Commission’s oversight of spot crypto markets and is still being coordinated with the Senate Banking Committee’s version.
Executive coordination: On February 2, the White House Crypto Policy Committee convened representatives from the crypto and traditional finance sectors to discuss market structure legislation and unresolved issues like stablecoin yields.
Regulatory cooperation: The SEC and CFTC announced they will jointly promote “crypto projects” to coordinate regulatory approaches for digital asset markets and reduce uncertainty caused by jurisdictional ambiguities.
EU: Promoting Implementation of Tax Transparency Directive
At the EU level, efforts are underway to ensure member states implement existing crypto tax transparency rules.
Violation handling: On January 30, the European Commission confirmed that 12 member states (including Belgium, Spain, the Netherlands) failed to transpose the DAC8 directive into national law on time. The directive requires crypto asset service providers to report customer transaction information to tax authorities. The EU has initiated infringement procedures, demanding these countries complete transposition within two months.
Goal: To ensure automatic exchange of crypto tax information across the EU to combat tax evasion.
Global Level: G20 Calls for Multilateral Regulatory Cooperation